APPLICATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY:
- Hydroxyapatite (HAP) production for use in dental and bone reconstruction, water purification, and compound materials for construction or for packaging
BENEFITS:
- Cost effective production of HAP and HAP-based composites
- Microbial production method allows shorter processing times and higher degrees of control
BACKGROUND:
- Calcium phosphate and its crystalline form, hydroxyapatite, are compounds useful in bone development, disease prevention, and other biomedical/commodity applications. Hydroxyapatite production is a labor and cost-intensive process that requires precise molecular ratios of precursors as well as long processing times. Development of microbial production pipelines can save time and energy and allows a greater degree of control.
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW:
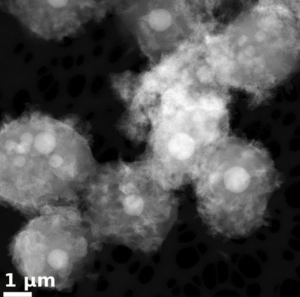
Berkeley Lab researchers developed an osteoblast-like yeast strain that can produce HAP in the presence of calcium and phosphate ions. They engineered the yeast strain Saccharomyces boulardii to hydrolyse urea. The yeast strain or “osteoyeast” showed similar characteristics to osteoblast bone deposition. In the presence of calcium and phosphate ions, osteoyeast forms internal vesicles carrying amorphous calcium phosphate. S. boulardii cells are also attached to external crystal structures, composed of crystalline calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite.
HAP has a wide range of applications. The Osteoyeast system creates HAP crystals that are physically attached to living yeast cells, allowing the unique advantage to functionalize cells for modification of biomaterial properties and applicability, including:
- pH-dependent drug delivery: hydroxyapatite crystals can bind and store proteins, small molecules, and DNA. At lower pH, the hydroxyapatite surface dissolves, enabling pH-dependent release of drugs
- biomedical applications: calcium phosphate is the main component of teeth and bone. The usage of engineered yeast cells can function as producers for biomimetic teeth and bone precursors or coating
- water purification: hydroxyapatite has been utilized to bind and remove contaminants from water.
- conduction material creation: calcium phosphate gel composites can be used as conductive material, for example TiO2-hydroxyapatite can be used as photocatalytic materials which have been utilized for nitric oxide (NO) removal.
DEVELOPMENT STAGE: Proven principle
PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS:
- Peter Ercius
- Yasuo Yoshikuni
- Yu-Wei Lin
- Isaak Mueller
STATUS: Patent pending.
OPPORTUNITIES: Available for licensing or collaborative research.
SEE THESE OTHER BERKELEY LAB TECHNOLOGIES IN THIS FIELD:
FlexBone: Osteo-mimetic Composites IB-2104