APPLICATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY: Analytical radiotracer high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) Research of metabolic pathways for biofuels, drug development and medical diagnostics ADVANTAGES: One hundred times more sensitive than existing radiotracer HPLC Can be manufactured with existing hardware ABSTRACT: Scientists at Berkeley Lab have developed an … [Read more...] about Highly Sensitive Detector for Radiotracer Chromatography IB-2765
Human Health/Precision Medicine
Simply Executed Nano-based Membrane Binding Sensor JIB-2649
APPLICATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY: Drug design, screening, and in vivo testing Clinical laboratory assays Biomedical research ADVANTAGES: Inexpensive implementation Can be achieved with a standard bench top spectrophotometer Scales up for high throughput Records real-time binding kinetics High signal-to-noise ratio Label-free detection ABSTRACT: Jay … [Read more...] about Simply Executed Nano-based Membrane Binding Sensor JIB-2649
Cell Surface Modification for Single Cell Analysis, Biosensing, and Tissue Engineering JIB-2703
APPLICATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY: Screening platforms for pharmaceuticals Biological production of biofuels Tissue engineering Cell-based biosensing ADVANTAGES: Faster and more biocompatible than existing methods Works for virtually all mammalian, plant, bacterial, and fungal cells Minimal to no effect on intracellular signaling pathways Enables … [Read more...] about Cell Surface Modification for Single Cell Analysis, Biosensing, and Tissue Engineering JIB-2703
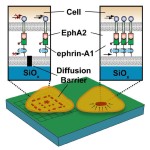
Cell Characterization by Phenotypic Analysis of Ligand Redistribution IB-2640
APPLICATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY: Drug design and testing Diagnosis and treatment of cancer and other diseases ADVANTAGES: Can be applied to living cells from biopsies Compatible with samples as small as a single cell May be scaled up to test multiple drugs simultaneously Analyzes phenotype rather than gene or protein expression Mimics and assesses … [Read more...] about Cell Characterization by Phenotypic Analysis of Ligand Redistribution IB-2640
Predictive Methodology and Tools for Nanotoxicology IB-2218b
Data Gathered using Berkeley Lab's Nanotoxicity Methodology (A) Numbers of genes whose expression levels changed after treatment with carbon nanomaterials at cytotoxic doses. (B-E) Venn diagrams comparing numbers of genes that showed expression changes. See the publication located at this link for more information on this image. APPLICATIONS: High throughput and … [Read more...] about Predictive Methodology and Tools for Nanotoxicology IB-2218b